Formula generator for VLOOKUP function
The VLOOKUP function is used to perform a vertical lookup in Excel. It searches down the first column of a specified range for a key and returns the value of a specified cell in the row found. The function takes four arguments: search_key (the value to search for), range (the table or range to search in), index (the column number in the range from which to return a value), and is_sorted (an optional argument to specify whether the range is sorted in ascending order).
Formula generator
Spreadsheet AI is the #1 AI for generating and comprehending Excel and Google Sheets formulas. With its advanced capabilities, it goes beyond the basics by providing support for VBA and custom tasks. Streamline your spreadsheet with Spreadshee AI
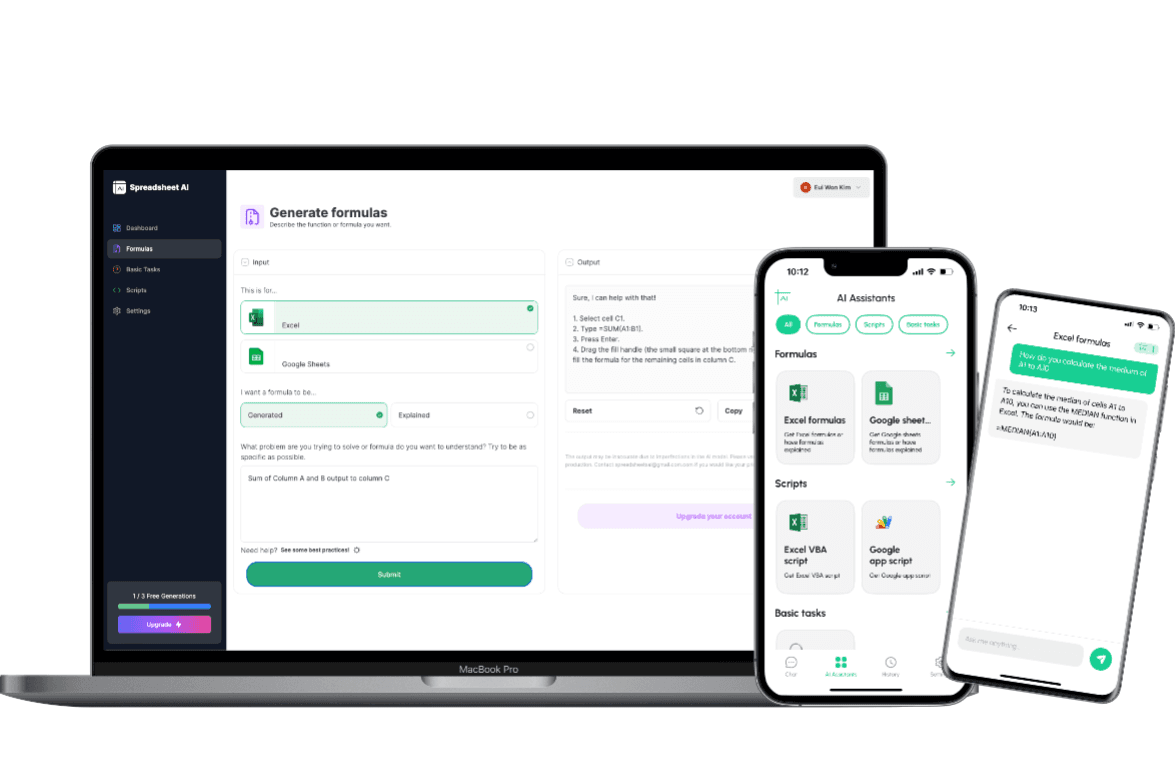
How to generate an VLOOKUP formula using AI.
To obtain information on the ARRAY_CONSTRAIN formula, you could ask the AI chatbot the following question: “To get the VLOOKUP formula from an AI chatbot, you could ask: 1. "How can I retrieve a value from a table in Excel based on a specific criteria?" 2. "Is there a formula in Excel that allows me to search for a value and return a corresponding value from another column?" 3. "What is the formula in Excel that performs a vertical lookup and returns a value from a table?" 4. "How can I find a specific value in a column and retrieve a corresponding value from a different column in Excel?" 5. "Is there a way to search for a value in a table and return a related value using a formula in Excel?"”
VLOOKUP formula syntax
The VLOOKUP function is used to search for a value in the first column of a table and retrieve a corresponding value from another column in the same row. The syntax for VLOOKUP is as follows: =VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup]) - lookup_value: The value you want to search for in the first column of the table. - table_array: The range of cells that contains the table you want to search in. - col_index_num: The column number (starting from 1) in the table from which you want to retrieve the value. - range_lookup: Optional. Determines whether you want an exact match or an approximate match. Use "TRUE" or 1 for an approximate match (default), and "FALSE" or 0 for an exact match. Example: =VLOOKUP(A2, B2:D10, 3, FALSE) This formula will search for the value in cell A2 within the range B2:D10, and return the corresponding value from the third column of the table. It will only return an exact match.
Use Cases & Examples
In these use cases, we use the VLOOKUP function to search for a specific value in the leftmost column of a range and retrieve a corresponding value from a different column.
Sales Analysis
Description
In this use case, we use the VLOOKUP function to analyze sales data. We have a table with product names in column A, and corresponding sales values in column B. We want to find the sales value for a specific product by searching for its name in the table.
Result
=VLOOKUP("Product Name", A1:B10, 2, FALSE)
Inventory Management
Description
In this use case, we use the VLOOKUP function to manage inventory. We have a table with product names in column A, and corresponding quantities in stock in column B. We want to find the quantity in stock for a specific product by searching for its name in the table.
Result
=VLOOKUP("Product Name", A1:B10, 2, FALSE)
Employee Database
Description
In this use case, we use the VLOOKUP function to retrieve employee information. We have a table with employee names in column A, and corresponding job titles in column B. We want to find the job title for a specific employee by searching for their name in the table.
Result
=VLOOKUP("Employee Name", A1:B10, 2, FALSE)
AI tips
Enhance Your Excel Efficiency with AI Tips: Discover our innovative Excel add-in feature, ‘AI Tips.’ Streamline your workflow and boost productivity as AI-powered suggestions offer real-time insights for optimal spreadsheet organization, data analysis, and visualization. Elevate your Excel experience with intelligent recommendations tailored to your unique needs, helping you work smarter and achieve more.
Provide Clear Context
When describing your requirements to the AI, provide clear and concise context about the data you have, the specific task you want to accomplish, and any relevant constraints or conditions. This helps the AI understand the problem accurately.
Include Key Details
Include important details such as column names, data ranges, and specific criteria that need to be considered in the formula. The more precise and specific you are, the better the AI can generate an appropriate formula.
Use Examples
If possible, provide examples or sample data to illustrate the desired outcome. This can help the AI better understand the pattern or logic you are looking for in the formula.
Mention Desired Functionality
Clearly articulate the functionality you want the formula to achieve. Specify if you are looking for lookups, calculations, aggregations, or any other specific operations.
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
- The VLOOKUP function is a built-in function in Excel that allows you to search for a specific value in a column of data and return a corresponding value from a different column in the same row.
- To use the VLOOKUP function, you need to provide four arguments: the value you want to look up, the range of cells where you want to search for the value, the column number in the range that contains the value you want to return, and an optional parameter that specifies whether you want an exact match or an approximate match.
- The syntax of the VLOOKUP function is: =VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup]).
- The range_lookup parameter in the VLOOKUP function is optional. If you set it to TRUE or omit it, Excel will perform an approximate match, where it looks for the closest value that is less than or equal to the lookup value. If you set it to FALSE, Excel will perform an exact match, where it looks for an exact match of the lookup value.
- No, the VLOOKUP function can only search for values in a single column. If you need to search for values in multiple columns, you can use the INDEX and MATCH functions together.